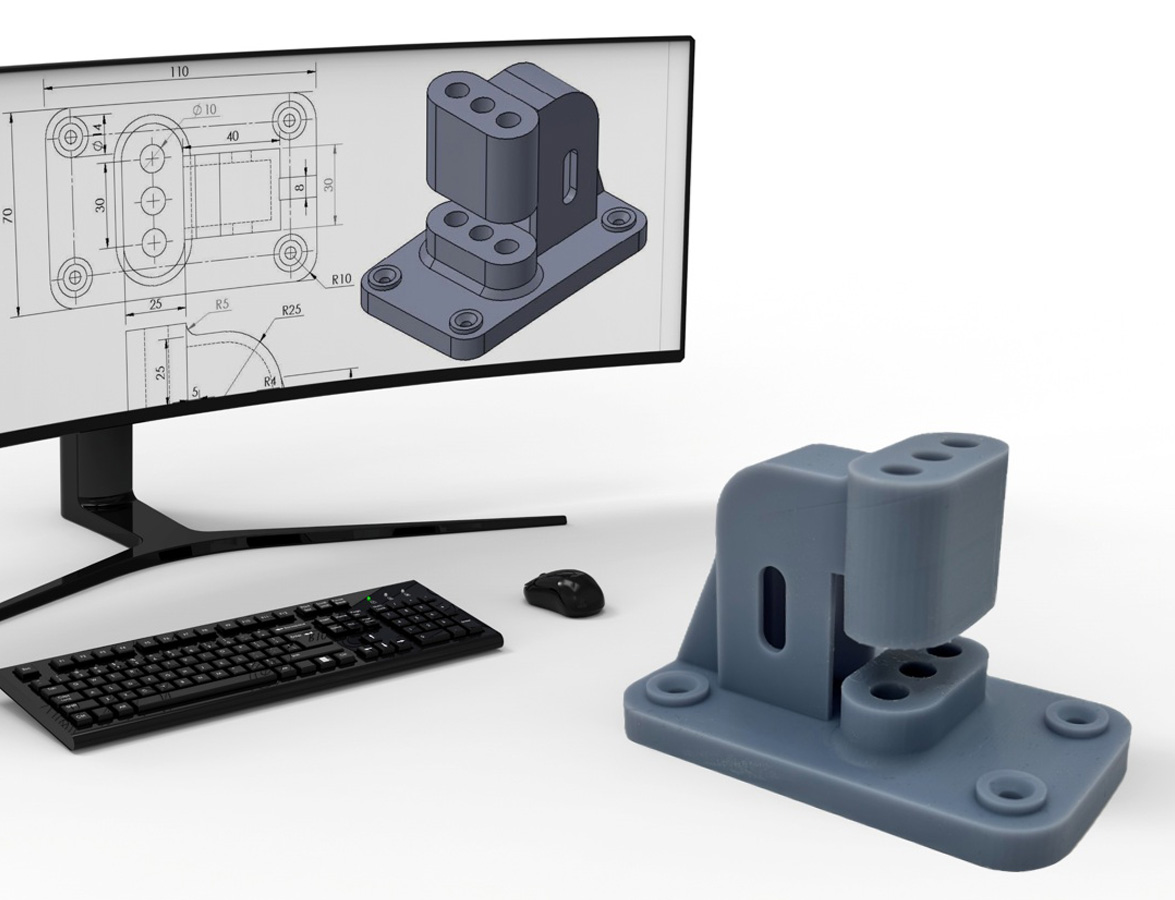
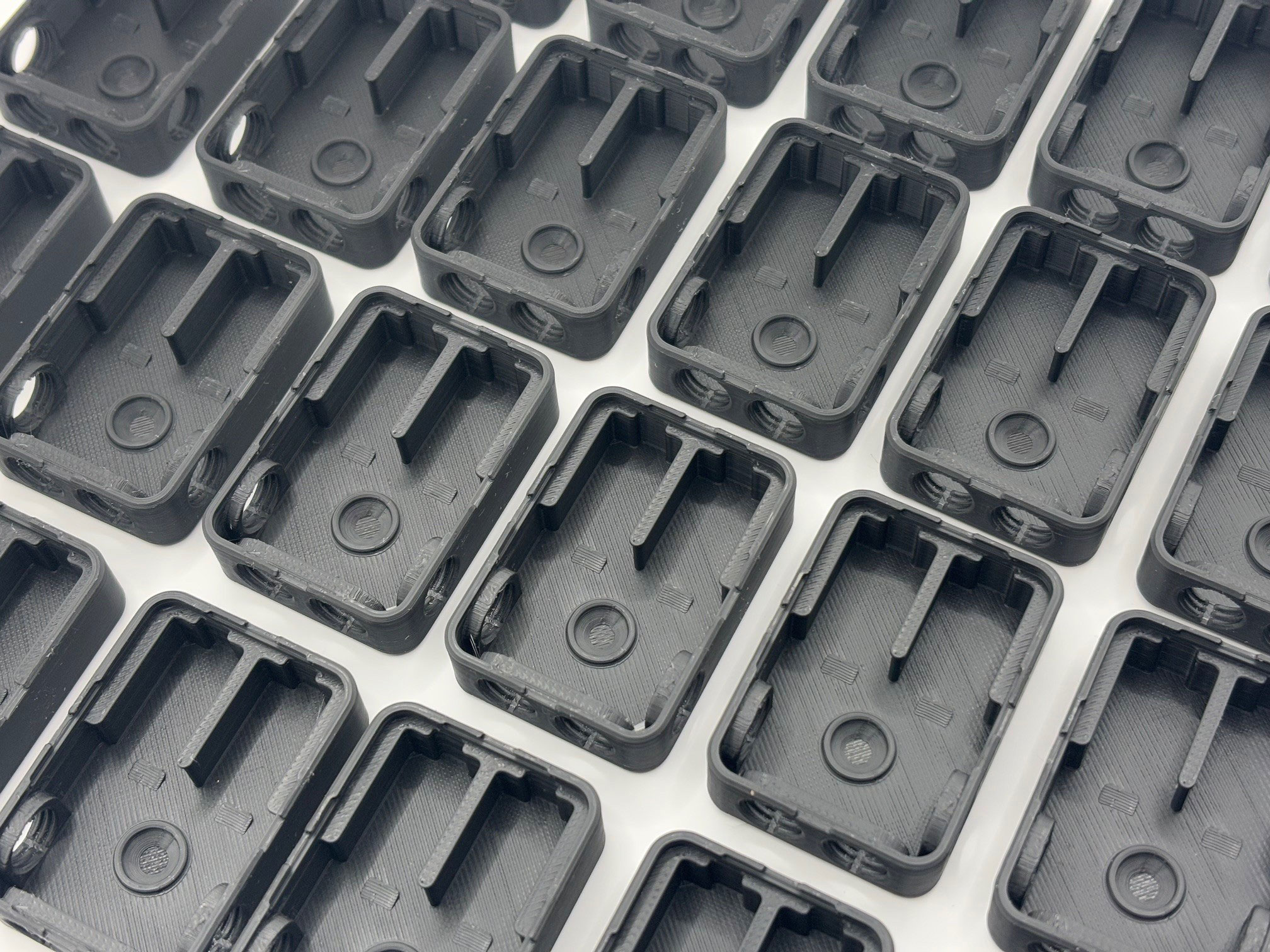
3D Printing, also referred to as Additive Manufacturing (AM), is the process of creating a physical object directly from a three-dimensional digital model.
At Bespoke 3D Printing, we turn your digital designs into high-quality physical creations with precision and care. Whether you need a single unit or a production run of 1,000, our 3D printing service provides a cost-effective solution for creating your plastic parts on demand.
Before you start printing, please read the information below to find out which of our services best meets your application.
Customization and Flexibility: 3D printing allows for unparalleled customization, enabling you to produce unique or highly specific parts without additional tooling costs.
Cost-Effective for Small Batches: Traditional manufacturing methods often involve expensive moulds or tooling, which are only economical for large-scale production.
Rapid Prototyping and Production: With 3D printing, designs can be turned into physical objects in a matter of hours.
Complex Geometries Made Simple: 3D printing can produce intricate and complex designs that would be impossible or highly expensive with traditional manufacturing techniques.
Reduced Material Waste: Unlike subtractive manufacturing methods (e.g., CNC machining), 3D printing only uses the material needed to create the part, significantly reducing waste and making it a more sustainable option.
On-Demand Production: 3D printing enables on-demand manufacturing, allowing you to produce parts exactly when needed.
Methods of Printing
FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling)
Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) is a 3D printing process where thermoplastic filament is heated, melted, and extruded through a nozzle. The printer builds objects layer by layer based on a digital 3D model, with the material solidifying upon cooling to form a precise and durable structure.
FDM printing is often chosen over SLA because it is more cost-effective, easier to use, and better suited for durable, functional parts. It works with a wide range of thermoplastic materials, requires less post-processing, and is ideal for larger, less intricate designs where surface finish and fine details are less critical.
SLA (Stereolithography)
Stereolithography (SLA) 3D printing uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin into solid layers. The laser traces the design on the resin's surface, hardening each layer sequentially. The process builds precise, high-resolution parts directly from a digital 3D model.
SLA printing is often preferred over FDM when higher precision, smoother surface finishes, and fine detail are required. SLA uses liquid resin cured by UV light, allowing for more intricate designs and smoother results. SLA prints with better dimensional accuracy and can handle more complex geometries.
Product Benefits
FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling)
Durability: FDM prints are typically made from strong, rigid materials, offering good mechanical strength for functional parts and prototypes.
Cost-Effectiveness: FDM printing is often more affordable than other methods, making it a popular choice for prototyping and low-volume production due to the relatively low cost of materials and printers.
Material Variety: FDM printers can work with a wide range of thermoplastic filaments, including specialty materials like flexible, composite, and high-temperature plastics, which expand the potential applications of printed products.
Layer Lines: While the layer-by-layer nature of FDM printing is visible, it can be minimized through post-processing techniques (sanding, smoothing) or printing with finer layer heights for more aesthetic finishes.
Large Print Volumes: Many FDM printers are capable of producing large-scale parts or models, offering flexibility for printing bigger objects compared to other 3D printing technologies.
SLA (Stereolithography)
High Precision and Detail: SLA printing offers exceptional resolution and fine detail, making it ideal for intricate designs, such as jewellery, dental models, and prototypes that require high accuracy.
Smooth Surface Finish: SLA prints typically have smooth, glossy surfaces with minimal visible layer lines, which reduces the need for extensive post-processing.
Excellent Dimensional Accuracy: SLA printing produces highly accurate parts with consistent geometry, which is important for applications that require tight tolerances and precise fitment.
Variety of Resin Options: SLA printers can use different types of resins, such as standard, flexible, castable, and high-temperature resins, allowing for a wide range of material properties to suit various applications.
Complex Geometries: SLA excels at printing complex geometries, including overhangs, fine details, and internal structures, which may be difficult or impossible for other printing methods to achieve without support structures.
Examples of Products
FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling)
Gear Wheels: Custom gears with specific tooth patterns and sizes.
Enclosures: Protective housings or cases for electronics.
Brackets and Mounts: Functional brackets and mounts.
Tool Handles: Ergonomic handles for hand tools.
Custom Fit Parts: Replacement or customized components.
Prototyping Models: Concept models of parts for testing.
SLA (Stereolithography)
Dental Models: High-precision dental moulds and aligners.
Jewellery Prototypes: Detailed and intricate jewellery designs.
Miniature Models: Highly detailed miniatures for models.
Medical Implants: Customized implants and prosthetics.
Consumer Product Prototypes: Prototype parts for consumer products.
Types of Material
FDM (Fused Deposition Modelling)
PLA (Polylactic Acid): Biodegradable, affordable, and available in a variety of colours and finishes.
Example Products: Tablet holders, non-functional tool prototypes, architectural models.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): Durable, heat-resistant, and strong.
Example Products: Brackets, custom casings/enclosures, gears, hinges.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol): Strong, UV/chemical & moisture resistant.
Example Products: Lab equipment components, camping gear components, custom water bottles.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane): Flexible, impact-resistant.
Example Products: Custom gaskets, prosthetic covers, orthotic insoles.
Carbon Fiber Reinforced Filaments: Filament infused with carbon fibre for increased stiffness and strength.
Example Products: Drone bodies, custom brackets, prototypes for automotive, aerospace, or industrial designs requiring high mechanical performance.
SLA (Stereolithography)
Photopolymer (Standard) Resin: Provides a good balance between detail and strength.
Example Products: Jewellery prototypes, miniatures/action figures, custom hearing aids.
Tough Resin: Durable and impact-resistant.
Example Products: Gears, hinges, protective casings, electrical connectors.
Flexible Resin: Rubber-like properties, allowing for bending and compression.
Example Products: Handles, grips, seals, gaskets.
High-Temperature Resin: Designed to withstand high heat without deforming.
Example Products: Light fixtures, moulds for wax casting, high-temperature electrical connectors.
Dental and Biocompatible Resin: FDA-compliant and safe for medical use.
Example Products: Custom dental implants, orthodontic aligners & retainers.
Rigid Resin: Reinforced with glass or other fillers for stiffness and high dimensional accuracy.
Example Products: Brackets, valve housings, camera casings, surgical tool handles.